Sibelius’ “The Origin of Fire”: A Cantata Based on Finnish Mythology
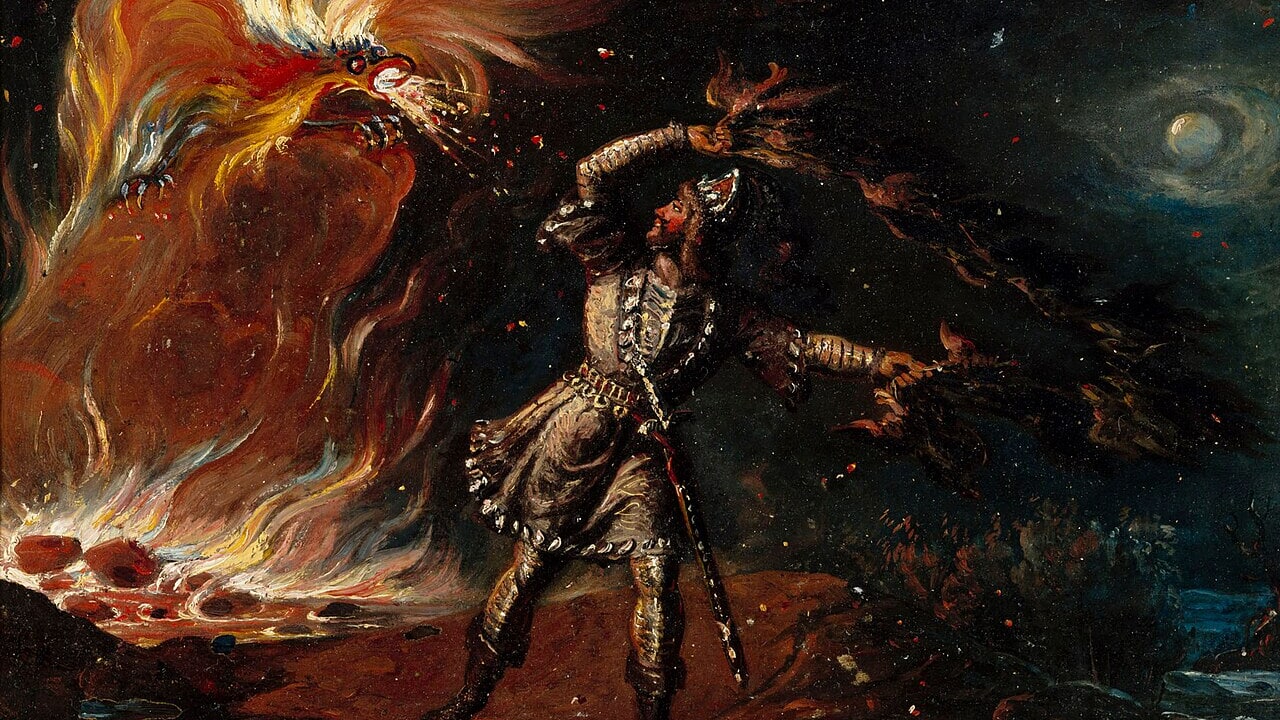
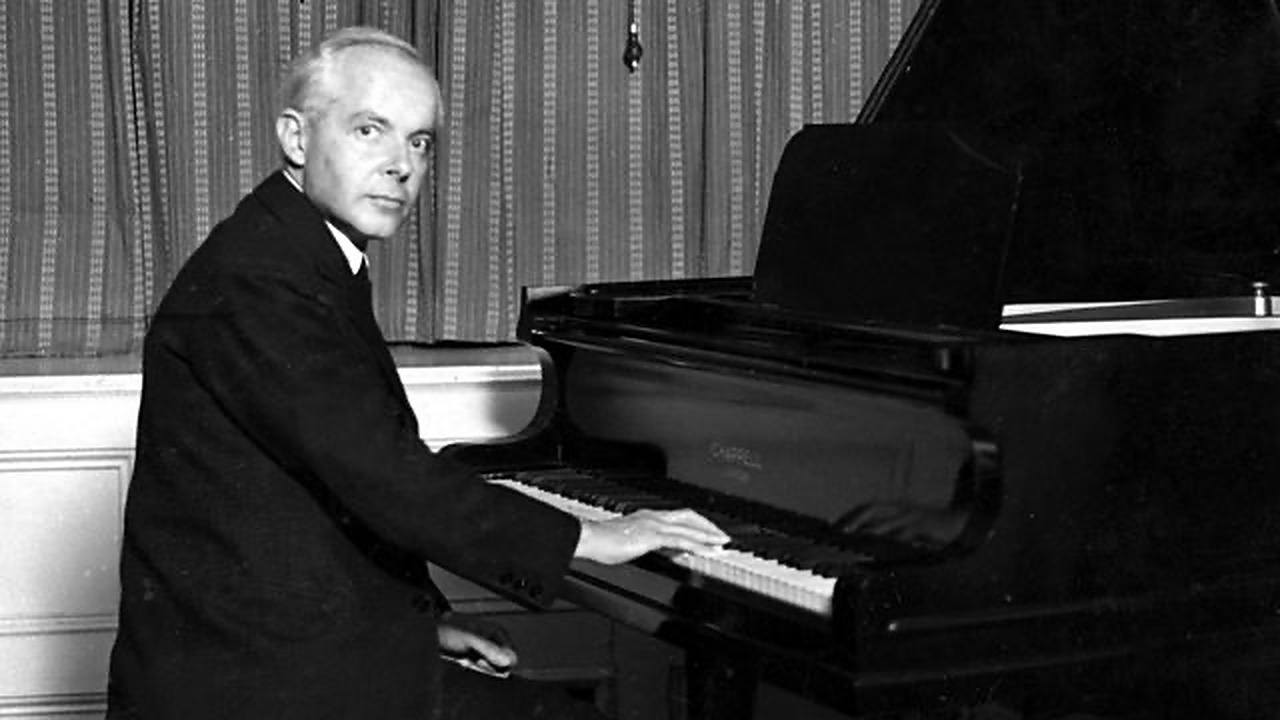
The Kalevala, the national epic poem of Finland, contains a myth with overtones of Prometheus. Ukko, the life-sustaining god of thunder, weather, and fertile fields, recreates fire after Louhi, the goddess of death and disease, steals it, along with the sun and moon. The story is the subject of Jean Sibelius’ 1902 cantata, The Origin of Fire (“Tulen synty”), Op. 32, scored for baritone, male chorus, and orchestra. The work was written for the opening …